In the fast-paced realm of e-commerce, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for businesses striving to maintain relevance and competitiveness. As we stride further into 2024, a plethora of cutting-edge technologies is poised to revolutionize the e-commerce landscape. From immersive shopping experiences to AI-driven personalization, here are seven futuristic e-commerce technology trends to watch out for this year:
You may be interested in the following articles as well.
1. Metaverse Integration
The concept of the metaverse, a virtual shared space created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and persistent virtual worlds, is increasingly influencing the e-commerce sphere. Brands are exploring immersive metaverse experiences, enabling customers to interact with products in virtual environments before making purchases. From virtual try-on of apparel to exploring lifelike virtual showrooms, metaverse integration is redefining online shopping.

Metaverse integration in e-commerce represents a paradigm shift, offering consumers and businesses alike a novel way to connect, explore, and transact within virtual environments. From virtual storefronts and digital showrooms to immersive shopping experiences, the possibilities are endless, and the implications are profound.
One of the most compelling aspects of metaverse integration is its ability to transcend the limitations of traditional online shopping experiences. In the metaverse, consumers can transcend geographical boundaries and physical constraints, immersing themselves in virtual environments that replicate the look and feel of real-world retail spaces. Imagine strolling through a bustling virtual marketplace, browsing shelves, interacting with products, and engaging with brands in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Moreover, metaverse integration opens up new avenues for experiential commerce, enabling brands to create immersive and interactive experiences that resonate with consumers on a deeper level. Whether it’s attending virtual fashion shows, participating in virtual product launches, or interacting with AI-powered virtual assistants, the metaverse offers a level of engagement and immersion that traditional e-commerce platforms struggle to match.
Furthermore, metaverse integration has the potential to democratize access to commerce, providing small and independent businesses with a platform to compete on a level playing field with industry giants. In the metaverse, the barriers to entry are lower, and the opportunities for innovation and creativity are limitless, empowering entrepreneurs to carve out their niche and build meaningful connections with customers in virtual spaces.
However, with great potential comes great responsibility, and the integration of the metaverse into e-commerce raises important questions about privacy, security, and digital ethics. As consumers spend more time in virtual environments, concerns about data privacy, virtual identity, and digital security become increasingly relevant. It’s imperative for businesses to prioritize transparency, accountability, and ethical practices to foster trust and confidence among consumers in the metaverse.
Metaverse integration represents a new frontier for e-commerce, offering boundless opportunities for innovation, engagement, and growth. By embracing the possibilities of the metaverse and leveraging immersive technologies to create compelling virtual experiences, businesses can redefine the future of online shopping and unlock new pathways to success in the digital age. As we navigate this exciting journey into the metaverse, let us embrace the transformative potential of technology to shape a more immersive, inclusive, and engaging e-commerce ecosystem for all.
2. Augmented Reality (AR) Shopping
Augmented Reality continues to reshape the e-commerce landscape by bridging the gap between online and offline shopping experiences. In 2024, AR technologies will become more sophisticated, allowing consumers to visualize products in their real-world environments with unprecedented accuracy. Whether it’s trying on virtual makeup or previewing furniture placement in a room, AR shopping enhances engagement and reduces purchase hesitation.

Augmented Reality (AR) shopping is rapidly transforming the e-commerce landscape, offering consumers an immersive and interactive way to experience products before making purchasing decisions. This article explores the evolution, benefits, and future prospects of AR shopping, highlighting its potential to revolutionize the online shopping experience.
- The Rise of AR Shopping
- Defining Augmented Reality: An overview of AR technology and its application in e-commerce.
- Evolution of AR Shopping: Tracing the evolution of AR shopping from novelty applications to mainstream adoption.
- Market Growth: Examining the increasing adoption of AR shopping solutions by retailers and brands across various industries.
- Immersive Product Visualization
- Bringing Products to Life: How AR enables consumers to visualize products in their real-world environments using smartphones or AR-enabled devices.
- Try Before You Buy: The ability to virtually try on clothing, accessories, and makeup before making purchases, reducing uncertainty and increasing confidence in buying decisions.
- Visualizing Home Furnishings: AR applications that allow consumers to preview furniture and home decor items in their living spaces, helping them make informed decisions about size, style, and placement.
- Enhancing the Shopping Experience
- Interactive Product Demos: Using AR to create interactive product demonstrations and tutorials that engage and educate consumers.
- Gamification: Incorporating gamified elements into AR shopping experiences to increase engagement and encourage repeat visits.
- Social Sharing: Integrating social media features that enable users to share AR experiences with friends and followers, driving word-of-mouth marketing and brand advocacy.
- Personalization and Recommendations
- Tailored Recommendations: Leveraging AI algorithms and consumer data to deliver personalized product recommendations based on individual preferences and shopping behavior.
- Contextual Targeting: Serving relevant AR experiences based on factors such as location, time of day, and browsing history, enhancing relevance and effectiveness.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Using AR to showcase complementary products and accessories, increasing average order value and maximizing revenue opportunities.
- Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
- Technical Constraints: Addressing technical challenges such as device compatibility, network connectivity, and rendering limitations to ensure a seamless AR shopping experience.
- User Experience: Designing intuitive and user-friendly AR interfaces that provide clear instructions and guidance for interacting with virtual products.
- Privacy and Security: Implementing robust data protection measures to safeguard consumer privacy and prevent unauthorized access to personal information.
- Future Trends and Opportunities
- Wearable AR Devices: Exploring the potential of wearable AR devices such as smart glasses to further enhance the AR shopping experience.
- Integration with Physical Retail: Integrating AR technology into brick-and-mortar stores to create seamless omnichannel shopping experiences.
- Augmented Reality Advertising: Leveraging AR for immersive advertising campaigns that capture consumer attention and drive engagement.
Augmented Reality (AR) shopping represents a paradigm shift in the way consumers interact with products and brands online. By offering immersive product visualization, enhancing the shopping experience, and delivering personalized recommendations, AR shopping has the potential to revolutionize e-commerce and redefine the future of retail. As technology continues to evolve and consumer expectations evolve, businesses must embrace AR shopping as a powerful tool for engaging customers, driving sales, and staying ahead of the competition in the digital age.
3. Voice Commerce
With the proliferation of smart speakers and virtual assistants, voice commerce is emerging as a game-changer in e-commerce. In 2024, advancements in natural language processing and AI algorithms will enable seamless voice-driven shopping experiences. Consumers can simply speak commands to browse products, place orders, and receive personalized recommendations, making shopping more convenient and intuitive than ever before.

In an era dominated by digital assistants and smart devices, voice commerce is emerging as a transformative force, reshaping the way consumers shop and interact with brands online. This article delves into the world of voice commerce, exploring its evolution, benefits, challenges, and future prospects in the e-commerce landscape.
- The Rise of Voice Commerce
- Defining Voice Commerce: An introduction to voice commerce and its significance in the context of e-commerce.
- Evolution of Voice Assistants: Tracing the evolution of voice-activated virtual assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri.
- Market Growth: Examining the rapid growth of voice commerce adoption and its impact on consumer shopping behavior.
- Seamless Shopping Experiences
- Hands-Free Convenience: The convenience of voice-activated shopping, allowing consumers to place orders, reorder products, and make purchases without lifting a finger.
- Natural Language Processing: Advancements in natural language processing (NLP) technology that enable virtual assistants to understand and fulfill complex shopping requests.
- Multi-Platform Integration: Integration with multiple devices and platforms, including smart speakers, smartphones, and smart TVs, to provide seamless shopping experiences across channels.
- Personalization and Recommendations
- AI-Powered Recommendations: Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to deliver personalized product recommendations and offers based on individual preferences and purchase history.
- Contextual Assistance: Providing contextually relevant information and assistance during the shopping journey, such as product details, reviews, and price comparisons.
- Predictive Insights: Anticipating consumer needs and preferences through data analysis and predictive modeling, enabling proactive recommendations and personalized shopping experiences.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement
- Conversational Commerce: Engaging customers in conversational interactions that mimic natural human dialogue, fostering a sense of rapport and connection.
- Interactive Promotions: Offering interactive promotions, quizzes, and games through voice-activated interfaces to drive engagement and brand awareness.
- Voice-Activated Loyalty Programs: Enabling customers to enroll in loyalty programs, redeem rewards, and track order status using voice commands, enhancing customer loyalty and retention.
- Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
- Accuracy and Reliability: Addressing challenges related to speech recognition accuracy, language understanding, and response reliability to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Privacy and Security: Implementing robust privacy and security measures to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access to personal data.
- Integration Complexity: Overcoming integration challenges with existing e-commerce platforms and backend systems to enable smooth voice commerce transactions.
- Future Trends and Opportunities
- Expansion of Voice-Activated Devices: The proliferation of voice-activated devices beyond smart speakers to include wearable devices, connected cars, and smart home appliances.
- Voice Search Optimization: Optimizing e-commerce websites and content for voice search queries to improve visibility and accessibility in voice-driven search results.
- Voice-Enabled Customer Support: Integrating voice technology into customer support systems to provide real-time assistance and resolve inquiries through voice interactions.
Voice commerce represents a significant opportunity for e-commerce businesses to engage customers, streamline transactions, and drive sales in an increasingly connected and voice-enabled world. By leveraging the power of natural language processing, AI-driven personalization, and conversational commerce, businesses can create seamless shopping experiences that cater to the evolving needs and preferences of today’s consumers. As voice commerce continues to evolve and mature, businesses must embrace this emerging trend as a key component of their omnichannel strategy, enabling them to stay ahead of the curve and deliver exceptional customer experiences in the digital age.
4. Hyper-Personalization
Leveraging big data and machine learning algorithms, hyper-personalization is taking personalized shopping experiences to new heights. In 2024, e-commerce platforms will harness customer data from various touchpoints to deliver highly tailored product recommendations, content, and promotions in real-time. By understanding individual preferences and behaviors, brands can foster deeper connections with customers and drive conversion rates.

In the vast landscape of e-commerce, where competition is fierce and consumer expectations are constantly evolving, hyper-personalization has emerged as a game-changer. Unlike traditional one-size-fits-all approaches, hyper-personalization leverages advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning algorithms to deliver tailor-made experiences to individual customers. From product recommendations to content personalization, hyper-personalization is revolutionizing the way businesses engage with consumers, driving higher conversion rates, increased customer loyalty, and ultimately, greater revenue growth.
At the heart of hyper-personalization lies the ability to harness vast amounts of data generated by consumer interactions across various touchpoints. Every click, search query, purchase, and social media interaction provides valuable insights into consumer preferences, behaviors, and intent. By analyzing this data in real-time, e-commerce platforms can create detailed customer profiles, allowing them to anticipate needs, predict preferences, and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
One of the most common applications of hyper-personalization in e-commerce is product recommendations. By analyzing past purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic information, e-commerce platforms can algorithmically generate personalized product suggestions that are highly relevant to each individual customer. These recommendations can be displayed prominently on product pages, in email campaigns, or as part of the checkout process, nudging customers towards additional purchases and increasing average order value.
Beyond product recommendations, hyper-personalization extends to content personalization, where brands tailor marketing messages, promotions, and content to match the interests and preferences of individual customers. By segmenting audiences based on demographics, browsing history, and engagement patterns, e-commerce platforms can deliver targeted content that resonates with each segment, driving higher engagement and conversion rates.
Hyper-personalization also plays a crucial role in enhancing the customer journey by providing seamless, frictionless experiences across multiple channels and devices. Whether a customer is browsing on a desktop computer, tablet, or smartphone, hyper-personalization ensures a consistent and personalized experience at every touchpoint. For example, a customer who abandons their shopping cart on a mobile device may receive a personalized email reminder with a discount code to incentivize them to complete their purchase.
Moreover, hyper-personalization enables businesses to engage with customers in real-time, responding to their needs and preferences in the moment. For example, an e-commerce platform may use AI-powered chatbots to provide personalized product recommendations, answer customer inquiries, and offer assistance with purchases. By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, these chatbots can deliver highly relevant and timely responses, enhancing the overall customer experience.
However, while hyper-personalization offers numerous benefits for businesses and consumers alike, it also raises important considerations around data privacy, transparency, and trust. As e-commerce platforms collect and analyze vast amounts of customer data, it’s essential for businesses to prioritize data security and compliance with privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Additionally, businesses must be transparent about how they use customer data and provide customers with control over their personal information, including the ability to opt-out of data collection and personalized experiences if desired.
Hyper-personalization represents a paradigm shift in the e-commerce landscape, enabling businesses to deliver tailored experiences that meet the unique needs and preferences of individual customers. By leveraging advanced data analytics, AI, and machine learning algorithms, e-commerce platforms can create highly personalized product recommendations, content, and experiences that drive engagement, loyalty, and ultimately, business growth. However, to realize the full potential of hyper-personalization, businesses must prioritize data privacy, transparency, and trust, ensuring that personalized experiences are delivered in a responsible and ethical manner.
5. Blockchain-Powered Supply Chain
The adoption of blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management in e-commerce. By providing transparent and immutable ledgers, blockchain enhances traceability, authenticity, and security across the entire supply chain ecosystem. In 2024, we’ll witness widespread implementation of blockchain-powered solutions, enabling seamless tracking of products from manufacturing to delivery, thus mitigating fraud and enhancing trust.
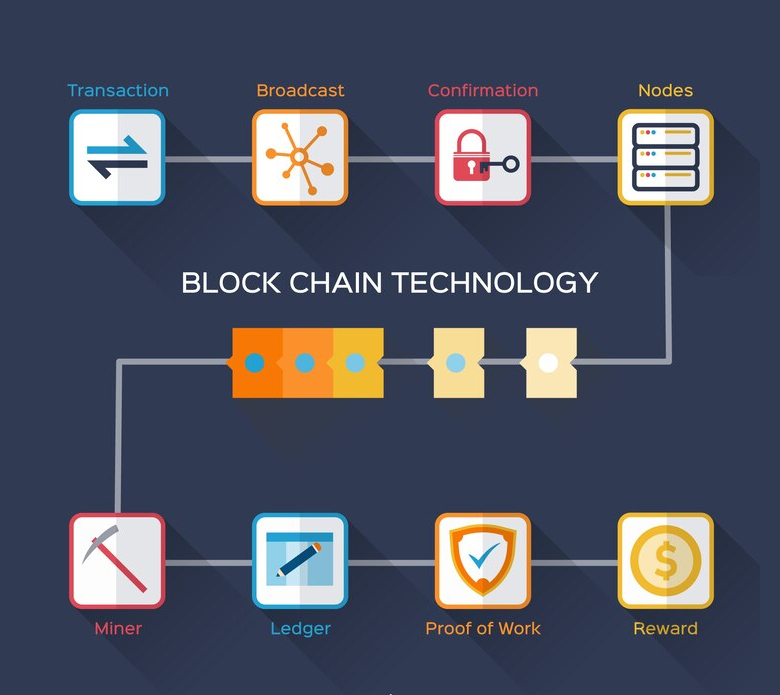
The traditional supply chain has long been plagued by inefficiencies, opacity, and trust issues, leading to challenges such as counterfeiting, supply chain fraud, and lack of transparency. However, with the advent of blockchain technology, there is a growing opportunity to transform the way supply chains operate, introducing unprecedented levels of transparency, security, and trust. This article explores the potential of blockchain-powered supply chains in e-commerce, examining how this innovative technology is reshaping the industry and driving sustainable growth.
Blockchain, often referred to as a distributed ledger technology, is a decentralized and immutable digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is securely encrypted and linked to previous transactions, creating a transparent and tamper-proof record of activity. In the context of supply chains, blockchain technology enables the secure and transparent tracking of goods as they move from production facilities to distribution centers to end consumers.
One of the key benefits of blockchain-powered supply chains is enhanced transparency. By recording every transaction on a shared ledger that is accessible to all participants in the supply chain, blockchain technology provides a real-time view of the movement and status of goods. This transparency not only enables stakeholders to track the provenance of products but also helps to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for optimization within the supply chain.
Moreover, blockchain technology enhances security by reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting. Each transaction recorded on the blockchain is cryptographically secured, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to alter or tamper with the data. This ensures the integrity of the supply chain and helps to prevent issues such as counterfeit products entering the market, protecting both consumers and brands from potential harm.
In addition to transparency and security, blockchain-powered supply chains also promote trust among participants. By providing a shared, immutable record of transactions, blockchain technology fosters a greater sense of accountability and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This increased trust enables stakeholders to work more closely together, share information more freely, and build stronger relationships throughout the supply chain ecosystem.
One of the most promising applications of blockchain technology in e-commerce is in the area of product provenance and authenticity. By leveraging blockchain-powered supply chains, brands can provide consumers with unprecedented visibility into the origins and journey of products, from raw materials to finished goods. This transparency not only helps to combat counterfeiting but also allows consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions based on factors such as ethical sourcing, sustainability, and quality.
Furthermore, blockchain technology can streamline and automate various aspects of supply chain management, reducing administrative overhead and operational costs. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can automate tasks such as inventory management, payment processing, and order fulfillment. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error and delays in the supply chain.
Despite its potential benefits, implementing blockchain-powered supply chains in e-commerce is not without challenges. One of the primary challenges is scalability, as blockchain networks may struggle to handle the high volume of transactions typically associated with e-commerce platforms. Additionally, there are concerns around interoperability and standardization, as different blockchain platforms may use incompatible protocols and data formats, hindering seamless integration across supply chain ecosystems.
Moreover, there are legal and regulatory considerations to navigate, particularly around data privacy and compliance with industry-specific regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Ensuring compliance with these regulations while maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain network is essential for the successful implementation of blockchain-powered supply chains in e-commerce.
Blockchain-powered supply chains have the potential to revolutionize the e-commerce industry by introducing unprecedented levels of transparency, security, and trust. By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses can create more resilient and efficient supply chain ecosystems, enhancing the customer experience, reducing costs, and driving sustainable growth. However, realizing the full potential of blockchain-powered supply chains requires overcoming technical, regulatory, and interoperability challenges, as well as fostering collaboration and adoption across the e-commerce ecosystem.
6. Social Commerce 2.0
Social commerce is evolving beyond basic buy buttons and shoppable posts to encompass immersive, interactive shopping experiences. In 2024, social media platforms will integrate advanced e-commerce features such as live shopping, gamified experiences, and social AR try-ons. By blurring the lines between social networking and online shopping, social commerce 2.0 enables brands to leverage the power of social influence and community engagement to drive sales.

- Defining Social Commerce 2.0
- Building on Tradition: Social Commerce 2.0 builds upon the foundation of its predecessor, enhancing social shopping experiences with advanced features and integrations.
- From Transactional to Experiential: Social Commerce 2.0 shifts the focus from simple buy buttons to immersive, interactive shopping experiences that foster engagement and loyalty.
- Embracing Emerging Platforms: Social Commerce 2.0 extends beyond traditional social media channels to incorporate emerging platforms such as live streaming, messaging apps, and virtual reality.
- Interactive Shopping Experiences
- Live Shopping Events: The rise of live shopping events, where brands and influencers showcase products in real-time, interact with audiences, and facilitate instant purchases.
- Gamified Experiences: Incorporating gamification elements into social shopping, such as interactive quizzes, challenges, and rewards, to engage and incentivize consumers.
- Augmented Reality Try-Ons: Allowing users to virtually try on products through augmented reality filters and effects, enhancing the online shopping experience and reducing purchase hesitation.
- Community Engagement and Influence
- Community Building: Social Commerce 2.0 emphasizes community-building, enabling brands to foster meaningful connections with customers and create brand advocates.
- Influencer Collaboration: Leveraging influencers and content creators to amplify brand messaging, drive product discovery, and increase engagement through sponsored content and collaborations.
- User-Generated Content: Encouraging user-generated content such as reviews, photos, and videos, which serve as authentic testimonials and social proof to influence purchasing decisions.
- Seamless Integration and Convenience
- Shoppable Posts and Stories: Integrating shoppable features directly into social media posts and stories, allowing users to discover and purchase products without leaving the platform.
- Social Payment Solutions: Introducing social payment solutions that enable seamless transactions within social media apps, simplifying the checkout process and reducing friction.
- Personalized Recommendations: Harnessing data analytics and AI algorithms to deliver personalized product recommendations based on user preferences, browsing history, and social interactions.
- Trust and Transparency
- Authenticity Assurance: Implementing measures to verify the authenticity of products and sellers, such as product authentication, verified badges, and customer reviews.
- Transparent Communication: Fostering open and transparent communication between brands and consumers, addressing inquiries, concerns, and feedback in a timely and responsive manner.
- Secure Transactions: Ensuring secure payment processing and data encryption to protect user privacy and financial information, building trust and confidence in social commerce transactions.
- Challenges and Considerations
- Privacy Concerns: Addressing privacy concerns related to data collection, tracking, and targeted advertising on social media platforms, and implementing measures to protect user privacy.
- Competition and Saturation: Navigating the increasingly competitive landscape of social commerce, where brands vie for consumer attention and engagement amidst a saturation of content.
- Platform Dependence: Mitigating the risks associated with platform dependence, where changes to social media algorithms or policies can impact reach, visibility, and sales for businesses.
Social Commerce 2.0 represents a new era of innovation and integration, elevating online shopping through social engagement, interactive experiences, and community-building. By embracing emerging technologies, fostering authentic connections, and prioritizing trust and transparency, brands can leverage the power of Social Commerce 2.0 to drive growth, loyalty, and customer satisfaction in the evolving e-commerce landscape. As we continue to explore the possibilities of Social Commerce 2.0, the future holds exciting opportunities for brands to connect with consumers in meaningful and impactful ways.
7. Robotic Automation in Warehousing and Fulfillment
Robotics and automation technologies are optimizing warehousing and fulfillment operations, enabling e-commerce businesses to meet growing consumer demands for fast and efficient delivery. In 2024, we’ll witness the widespread adoption of autonomous mobile robots, robotic pickers, and automated sorting systems in fulfillment centers. These innovations streamline order processing, reduce labor costs, and accelerate order fulfillment, ultimately enhancing the overall customer experience.
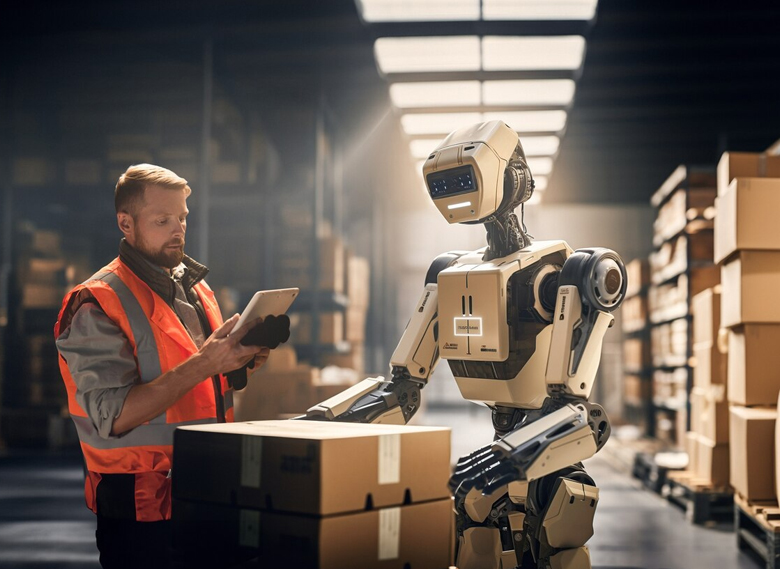

- The Evolution of Robotic Automation
- From Science Fiction to Reality: A brief history of robotic automation in warehousing and fulfillment, from early prototypes to modern-day applications.
- Advancements in Robotics Technology: Key technological innovations driving the adoption of robotics in logistics, including sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning.
- Market Growth: The rapid expansion of the robotics market in warehousing and fulfillment, fueled by the rise of e-commerce and the need for greater efficiency and scalability.
- Robotic Solutions in Warehousing
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Agile, wheeled robots equipped with sensors and navigation systems that can autonomously navigate warehouse environments, picking and transporting goods to designated locations.
- Robotic Arms: Versatile robotic arms capable of performing a wide range of tasks, including picking, packing, sorting, and palletizing, with speed and precision.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Vehicles equipped with guidance systems that can navigate predefined paths within warehouses, transporting goods between storage areas, docks, and production lines.
- Optimizing Fulfillment Operations
- Increased Efficiency: Robotic automation streamlines fulfillment processes, reducing order processing times, minimizing errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Scalability: Robots can quickly adapt to fluctuations in demand, allowing warehouses to scale operations up or down as needed without the need for additional human labor.
- 24/7 Operations: Robots can operate continuously without breaks, enabling warehouses to fulfill orders faster and more efficiently, even during peak periods.
- Enhancing Worker Safety and Ergonomics
- Collaborative Robotics: Robots designed to work alongside human workers, assisting with repetitive or physically demanding tasks while enhancing worker safety and ergonomics.
- Injury Reduction: By automating tasks that pose risks to human workers, such as heavy lifting or repetitive motion, robotic automation can help reduce workplace injuries and improve employee well-being.
- Ergonomic Design: Robotic solutions are engineered with ergonomics in mind, minimizing strain and fatigue on human workers and creating a safer and more comfortable working environment.
- Challenges and Considerations
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of implementing robotic automation can be significant, requiring careful cost-benefit analysis and long-term planning.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating robotic solutions with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and processes requires careful coordination and expertise to ensure seamless operation.
- Maintenance and Support: Ongoing maintenance and support are essential to keep robotic systems running smoothly, requiring specialized skills and resources.
- Future Trends and Opportunities
- AI and Machine Learning: Continued advancements in AI and machine learning will enable robots to become more intelligent and adaptive, optimizing warehouse operations in real-time.
- Robotics as a Service (RaaS): The emergence of robotics as a service models will democratize access to robotic automation, allowing smaller businesses to leverage robotic solutions without significant upfront investment.
- Collaboration and Interoperability: Greater collaboration and interoperability between different robotic systems and technologies will enable warehouses to deploy integrated solutions that offer greater flexibility and efficiency.
Robotic automation is transforming warehousing and fulfillment operations, offering unparalleled levels of efficiency, scalability, and safety. By leveraging robotic solutions, warehouses can streamline processes, enhance worker productivity, and meet the demands of an increasingly competitive e-commerce landscape. While challenges remain, the future of robotic automation in warehousing is bright, with continued advancements in technology and greater collaboration driving innovation and growth in the logistics industry.
Conclusion
As we embark on this journey into the future of e-commerce, embracing these transformative technologies will be paramount for businesses aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. By harnessing the power of the metaverse, AR, voice commerce, hyper-personalization, blockchain, social commerce 2.0, and robotic automation, e-commerce enterprises can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and customer engagement in 2024 and beyond.